The role of cyber security in the digital economy: an essential guide

In today’s digital economy, cyber security has become a vital and non-negotiable element of running a company. The term may sound simple, but it involves more than just protecting our integrity or confidentiality and taking part in securing our digital assets and online presence. In this post, we will cover the role of cyber security with continuous innovations and developments and its relevance in today’s fast-paced tech advancements!
Where do we focus when deciding to protect our systems from intruders? By understanding potential risks and ensuring preventative measures are in place.
Areas to focus on in cyber security
Protect data and assets
Protecting the data from unauthorized access, theft, and manipulation becomes their responsibility. Deploying encryption, access control and firewalls are the tools they use to safeguard sensitive information and digital resources.
Build trust and confidence
A robust cyber security posture ensures that individuals feel safe about their online existence. Whether they are individuals, consumers or investors, some policies must be implemented to keep the trust for a better digital economy.
Continuity and reliability
With continuous efforts, cyber security experts maintain critical digital services. This keeps the availability of online services and platforms reliable for the general public.
Upholding compliance and security
Data protection, privacy laws, and cyber security practices are for everyone. It becomes the responsibility of cyber security leaders to follow these practices. This ensures the rate of cyber crimes in the digital landscape.
Principles of designing unique computing systems
Secure architecture: create a well-defined and secure architecture for the computing system, which identifies potential vulnerabilities and threats and implements appropriate security controls at each level of the system’s design.
Isolation and segmentation: trying to isolate and segment components and data to contain potential breaches and limit the impact of security incidents. Implementing a trusted execution environment to isolate critical processes and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access is one of the most effective ways to control the potential risks.
Hardware security: use secure hardware components and technologies that offer built-in security features, such as hardware-based encryption and specific boot mechanisms. Ensuring the system’s boot process and firmware is a powerful tool to secure and resist tampering or unauthorized modifications.
Cryptography: Using robust cryptographic algorithms and protocols to protect data stored, in transit, and during processing. In addition, implement constant monitoring and threat detection mechanisms to respond to security incidents promptly.
Redundancy and failover: Design the system with redundancy and failover capabilities to ensure continuous operation despite hardware failures or cyber-attacks.
Role-based access control: Employ role-based access control (RBAC) to manage privileges and restrict access to sensitive resources based on roles and responsibilities.
Security testing: Conduct rigorous security testing, including penetration and vulnerability assessments, to identify and remediate potential weaknesses. Regular updates and patch management are a great way to keep all software, firmware and hardware components updated with the latest updates and security patches.
Incident response planning: A comprehensive and adaptable incident response plan to outline the steps to be taken in case of a security breach or cyber-attack. Regularly test and update the project to ensure its effectiveness.
Education and awareness: Educate users about cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing emails, using strong passwords, and reporting suspicious activities.
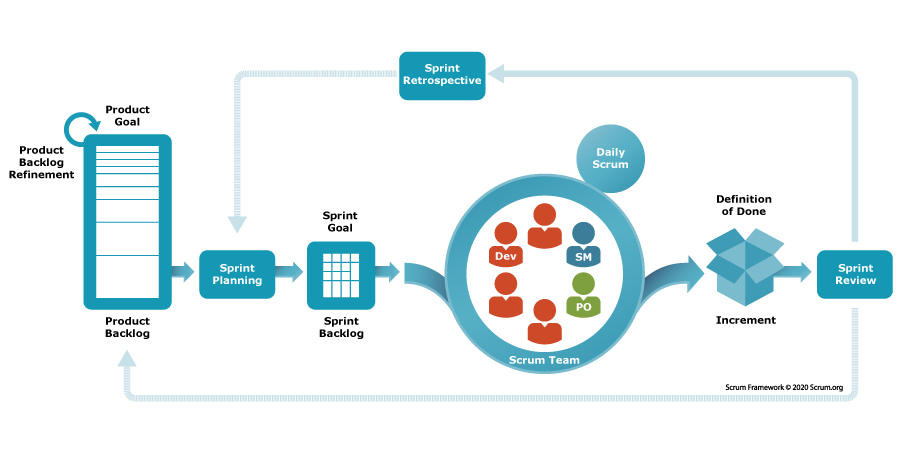
Agile security software development
Agile methodologies in security software development involve iterative work, continuous feedback, and risk-based approaches. Secure coding practices, regular security testing, threat modelling, secure deployment practices, and retrospective analyses form part of the ongoing improvement process. A designated security product owner ensures security concerns are addressed and prioritized. Here’s an example of Microsoft Agile software’s Scrum.
Development of BI platforms for cyber security predictive analysis
BI platforms can help predict potential cyber threats by combining data collection and integration, data cleaning and transformation, and data warehousing with predictive analytic models. Incorporating external threat intelligence feeds and real-time monitoring heightens the analysis and creates advanced early warning systems.
The actual role and the dimension of cyber security can not be explained in a few words and go beyond mere protection of digital data. With flaws, vulnerabilities, new threats, zero-day exploitations and ever-evolving hackers, we can only survive with a proper security system. Understanding cyber security’s depth is crucial for any digital ecosystem in a world persistently under potential risks.
Stay tuned!


